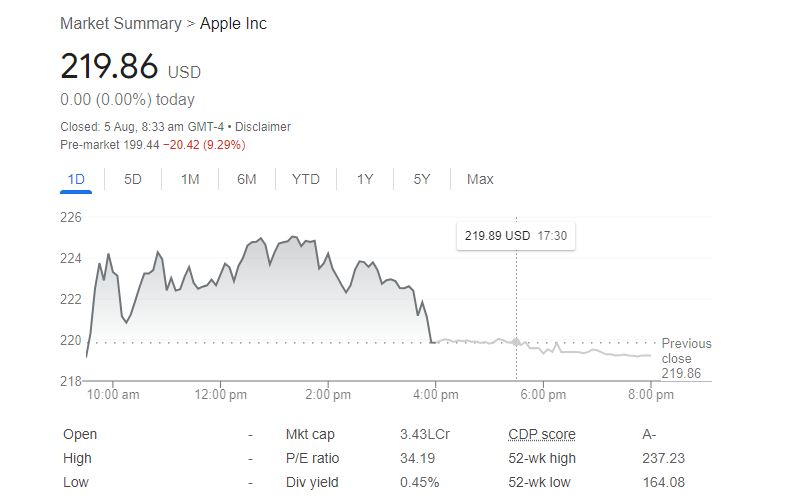
The trajectory of Apple Inc. (AAPL) stock has been a focal point for investors, analysts, and tech enthusiasts alike. As one of the most valuable companies in the world, Apple’s stock performance is a barometer for the broader tech industry and a significant component of major market indices.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of the rise and fall of Apple stock, considering various factors from a FintechZoom perspective.
Introduction to Apple
Apple Inc., founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, revolutionized the personal computer industry with the introduction of the Apple II.
Over the decades, Apple expanded its product line to include groundbreaking devices such as the iPod, iPhone, iPad, and MacBook, transforming the company into a tech giant with a loyal customer base and a market capitalization that has often surpassed $2 trillion.
The performance of Apple’s stock reflects its innovation-driven growth, strategic management decisions, and ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
However, like any stock, AAPL has experienced significant fluctuations influenced by a multitude of factors, including product launches, financial results, market trends, and broader economic conditions.
The Ascent: Factors Contributing to Apple’s Stock Rise
1. Innovation and Product Ecosystem
Apple’s ability to innovate has been a critical driver of its stock performance. The launch of the iPhone in 2007 marked a turning point, establishing Apple as a leader in the smartphone market. Subsequent iterations of the iPhone, along with the introduction of the iPad, Apple Watch, and AirPods, reinforced Apple’s position as a market leader.
The interconnected products and services ecosystem, including iCloud, Apple Music, and the App Store, created a seamless user experience that encouraged customer loyalty and recurring revenue streams. This ecosystem has become a fortress that competitors find hard to penetrate, making customers stick with Apple products for the long haul.
2. Financial Performance and Revenue Growth
Consistently strong financial performance has been a hallmark of Apple’s rise. Record-breaking quarterly earnings, driven by robust sales of iPhones and other devices, have instilled confidence among investors. Apple’s ability to generate significant cash flow has enabled it to invest in research and development, acquire complementary businesses, and return value to shareholders.
Diversification into services and wearables has also contributed to revenue growth. Services such as Apple Music, Apple TV+, and Apple Pay have become significant revenue contributors, reducing Apple’s reliance on hardware sales. The company’s shift towards services has provided a steady and growing revenue stream, insulating it from the cyclical nature of hardware sales.
3. Global Expansion and Market Penetration
Apple’s strategic expansion into international markets, particularly China and India, has opened new avenues for growth. Despite challenges, these markets have provided substantial revenue opportunities. China, for example, has become one of Apple’s largest markets, contributing significantly to its overall sales.
The establishment of retail stores worldwide has enhanced brand visibility and customer engagement, further boosting sales and stock performance. Apple’s iconic retail stores, known for their sleek design and excellent customer service, have become a key part of its brand identity and a powerful sales channel.
4. Share Buybacks and Dividends
Apple’s capital return program, including share buybacks and dividends, has been instrumental in supporting its stock price. By repurchasing shares, Apple has reduced the number of outstanding shares, increasing earnings per share (EPS) and delivering value to shareholders.
Regular dividend payments have made Apple stock attractive to income-focused investors, contributing to sustained demand. Apple’s disciplined capital return strategy has reinforced investor confidence and supported its stock price during periods of market volatility.
Fintechzoom Meta Stock: A Comprehensive Guide
The Fall: Factors Leading to Declines in Apple’s Stock
1. Market Saturation and Competitive Pressures
The smartphone market, a significant revenue source for Apple, has become increasingly saturated. With limited room for significant growth, competition from rivals such as Samsung, Huawei, and emerging brands has intensified. These competitors have closed the innovation gap, offering high-quality devices at lower prices.
Innovations have become incremental rather than revolutionary, leading to longer replacement cycles for devices like iPhones. This trend has affected sales growth and investor sentiment. Consumers are holding on to their devices longer, waiting for compelling new features before upgrading.
2. Supply Chain Disruptions
Apple’s reliance on a complex global supply chain has made it vulnerable to disruptions. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted these vulnerabilities, causing delays in production and supply shortages. Lockdowns, factory closures, and logistics challenges disrupted Apple’s ability to meet demand.
Geopolitical tensions, such as the US-China trade war, have also impacted Apple’s supply chain and raised concerns about future supply stability. Tariffs and export restrictions have increased costs and created uncertainties for Apple’s manufacturing operations.
3. Regulatory and Legal Challenges
Apple has faced regulatory scrutiny and legal challenges across various jurisdictions. Antitrust investigations have posed significant risks, particularly related to the App Store’s practices. Regulators have questioned Apple’s control over its app ecosystem and its policies regarding app distribution and fees.
Legal disputes over intellectual property and patent infringements have also resulted in financial penalties and operational constraints. High-profile lawsuits with companies like Qualcomm and Epic Games have drawn attention to Apple’s business practices and exposed it to potential liabilities.
4. Economic Conditions and Market Volatility
Broader economic conditions have affected consumer spending and investment sentiment, including inflation, interest rate hikes, and economic downturns. As a high-growth tech stock, Apple is particularly sensitive to macroeconomic factors. Economic uncertainty can dampen consumer confidence and reduce discretionary spending on premium devices.
Market volatility and investor rotation from growth to value stocks have also contributed to periods of decline in Apple’s stock price. During market corrections, high-valuation tech stocks like Apple often experience sharper declines as investors reassess risk and move towards safer assets.
Improved Financial Security With Robust Identity Verification For Fintech
Market Sentiments
Apple’s product innovation and dedicated customer base have long driven stock prices. With the introduction of AR products and AI integration, Apple is poised to maintain its leadership in next-gen tech, likely boosting revenue and profit growth over the long term.
However, these predictions must be weighed against overall market conditions and macroeconomic indicators that could impact sales growth or profitability. Increased regulatory scrutiny or competition from other tech companies could erode investor trust, while global economic factors like shifting trade dynamics or post-pandemic recovery could affect consumer spending patterns or cause supply chain disruptions.
Investors can use FintechZoom to monitor market sentiment and identify emerging trends, to reduce risks and to capitalize on opportunities during market instability. Its insights enable informed decisions, maximizing investments, and achieving financial goals more securely.
FintechZoom allows investors to analyze Apple’s performance against its peers and competitors, helping assess its competitive landscape and strategic positioning. Predictive analytics offer insights into potential events’ effects on stock performance, while sentiment and market trend analysis provide a comprehensive view of Apple stock’s current and future prospects.
Strategic Adaptations and Future Outlook
1. Innovation and Diversification
Apple continues to invest heavily in research and development to maintain its competitive edge. Emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and autonomous systems represent potential growth areas. Apple’s rumored AR glasses and advancements in machine learning and AI could unlock new market opportunities.
Diversification into services and wearables will remain a key strategy. Continued expansion of the services ecosystem and innovations in health-focused wearables like the Apple Watch are expected to drive future growth. Apple’s health initiatives, including advanced health monitoring features and partnerships with healthcare providers, position it to capitalize on the growing digital health market.
2. Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Apple’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices resonates with increasingly conscientious consumers and investors. Initiatives such as carbon neutrality and responsible sourcing of materials enhance Apple’s brand reputation. Apple’s efforts to reduce its environmental impact, such as using recycled materials and investing in renewable energy, are integral to its corporate social responsibility strategy.
Transparency in data privacy and security practices also positions Apple favorably in an era of growing concerns over digital privacy. Apple’s emphasis on user privacy, such as features that limit tracking and enhance data security, differentiates it from competitors and builds consumer trust.
3. Global Market Opportunities
Continued focus on emerging markets, particularly India, will be crucial. Tailoring products to meet the needs and price points of these markets can unlock significant growth potential.
Apple’s recent efforts to expand manufacturing in India and launch region-specific products demonstrate its commitment to capturing market share in this high-growth region.
Strengthening relationships with local partners and navigating regulatory landscapes effectively will be key to success in these regions. Collaborations with local carriers, retailers, and app developers can enhance Apple’s market penetration and adapt its offerings to local preferences.
4. Financial Resilience
Apple’s robust financial health, characterized by substantial cash reserves and strong cash flow, provides flexibility to weather economic uncertainties and invest in strategic initiatives. The company’s financial strength enables it to pursue acquisitions, invest in cutting-edge technologies, and return capital to shareholders even during challenging times.
Maintaining a balanced approach to capital return programs and strategic acquisitions can enhance shareholder value and support long-term growth. Apple’s disciplined financial management, including prudent cash allocation and debt management, reinforces its ability to navigate market volatility and sustain growth.
What is FintechZoom, Benefits, Features, Requirements
Conclusion
The rise and fall of Apple stock reflect the dynamic nature of the tech industry and the multiple factors influencing stock performance. While facing challenges from market saturation, supply chain disruptions, and regulatory scrutiny, Apple’s strengths in innovation, financial resilience, and strategic adaptability position it well for future growth.
Investors should remain aware of the opportunities and risks associated with Apple stock, leveraging comprehensive analysis and a forward-looking perspective to make informed decisions.
Ultimately, Apple’s journey offers valuable insights into the potential and volatility inherent in the tech sector, underscoring the importance of staying attuned to market developments.
