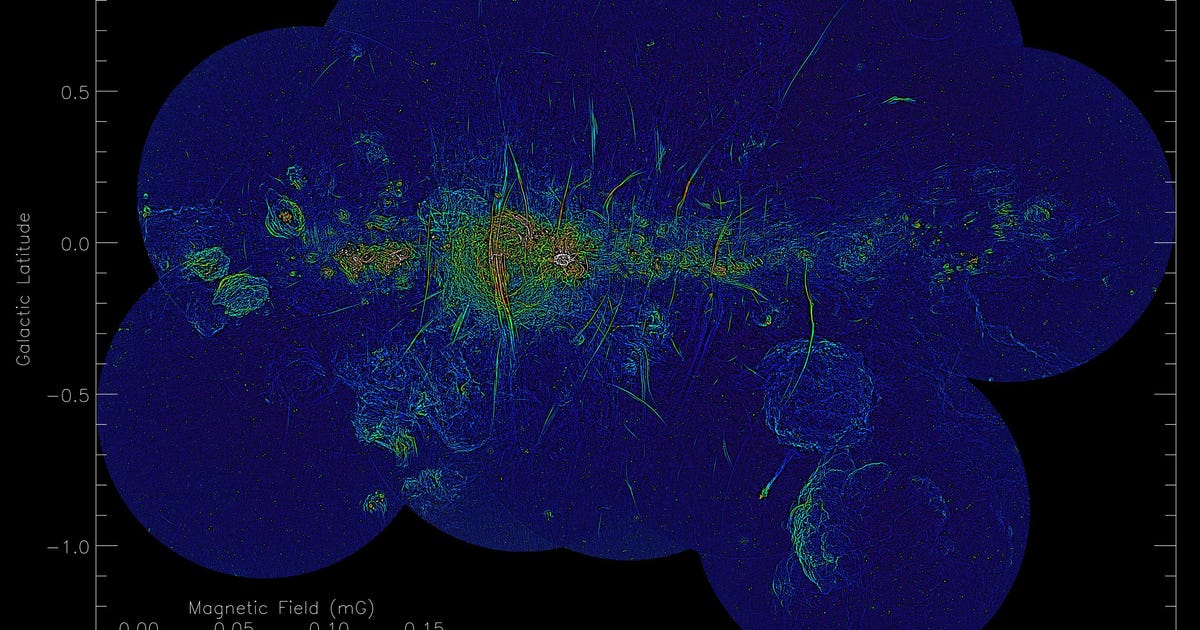
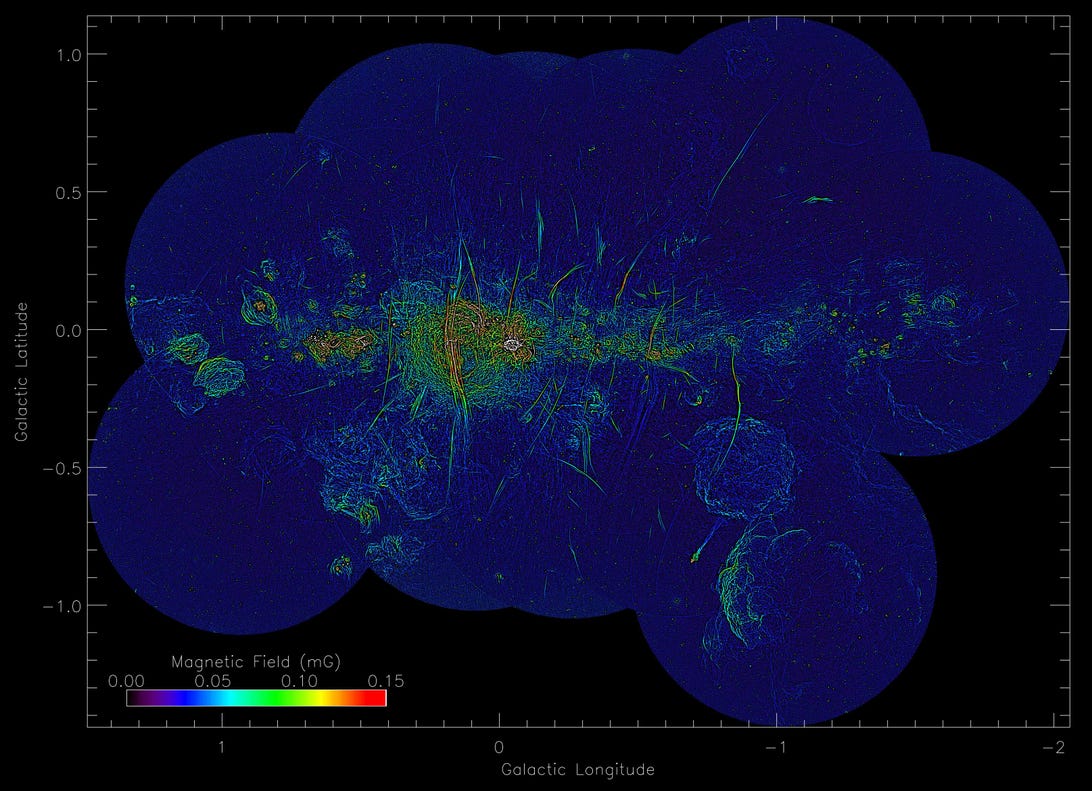
A picture appearing the distribution of the strengths of magnetic fields.
Northwestern College/Saoro/Oxford College
Within the early Nineteen Eighties, scientists imaged the middle of our galaxy 25,000 light-years from Earth. To their marvel, they stumbled upon a cluster of “strands” 150 light-years lengthy striking out in an oddly arranged trend. For years, they scrutinized the stringy forces, seeking to perceive what they’re and why they are there.
No, those galactic noodles (almost certainly) don’t seem to be the paintings of extraterrestrial beings. However they later printed themselves to be some form of magnetic wiring, catching space-borne cosmic ray electrons and forcing the debris to gyrate round their fields at just about the rate of sunshine. If anything else, the enigma escalated.
Speedy-forward to these days. The similar researcher who led the primary imaging undertaking determined to create an up to date model. In a paper revealed on-line Wednesday and accredited to The Astrophysical Magazine Letters, he gifts his effects: a completely impressive landscape of radio emission knowledge stemming from the Milky Manner’s heart.
Cosmic phenomena akin to big name bursts, stellar nurseries and supernova graveyards stained the image with good streaks, however maximum strikingly, the picture unveiled 10 occasions extra perplexing strands than sooner than. “It is like fashionable artwork,” Farhad Yusef-Zadeh, an astrophysicist at Northwestern College and lead writer of the paper, stated in a observation. “Those pictures are so gorgeous and wealthy, and the thriller of all of it makes it much more fascinating.”
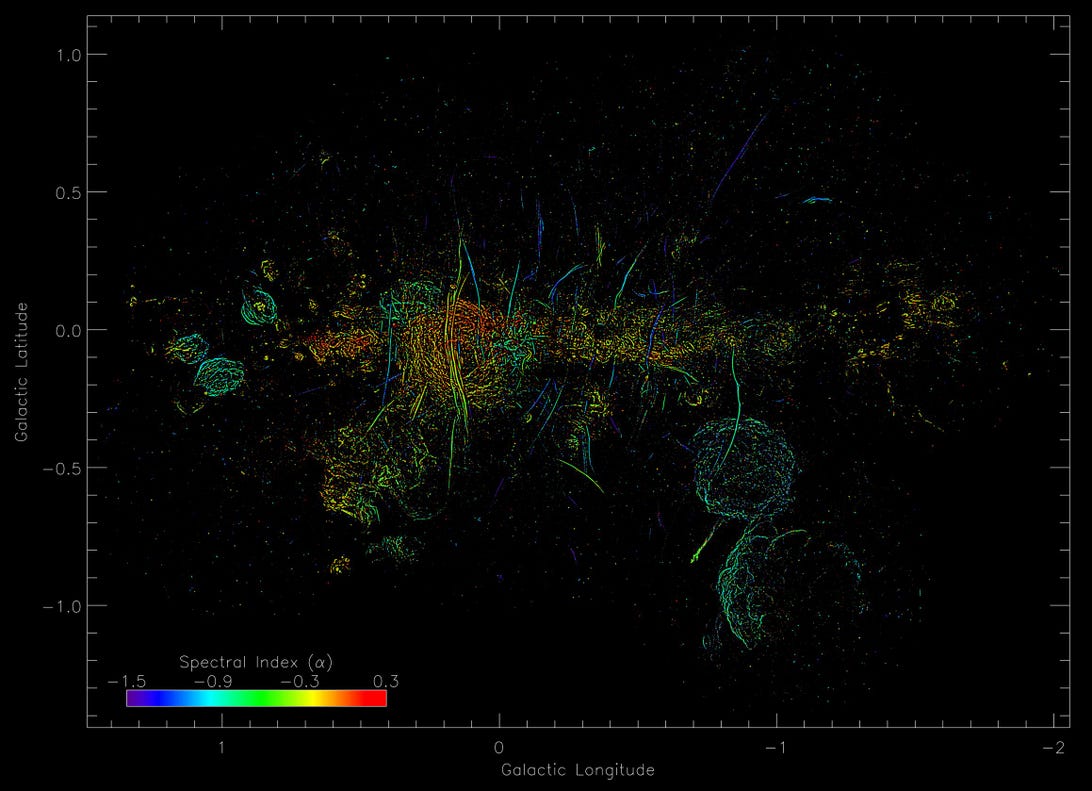
A picture appearing the spectral index for the filaments.
Northwestern College/Saoro/Oxford College
He calls the more moderen image a “watershed in furthering our figuring out of those buildings,” for the reason that preliminary, somewhat sparser selection of filaments was once too small to attract any actual conclusions about their starting place and function.
Photographing a large galaxy
It took 3 years of surveying the sky and 200 hours the usage of the Meerkat telescope on the South African Radio Astronomy Observatory for Yusef-Zadeh’s group to generate actual observations of 20 separate sections.
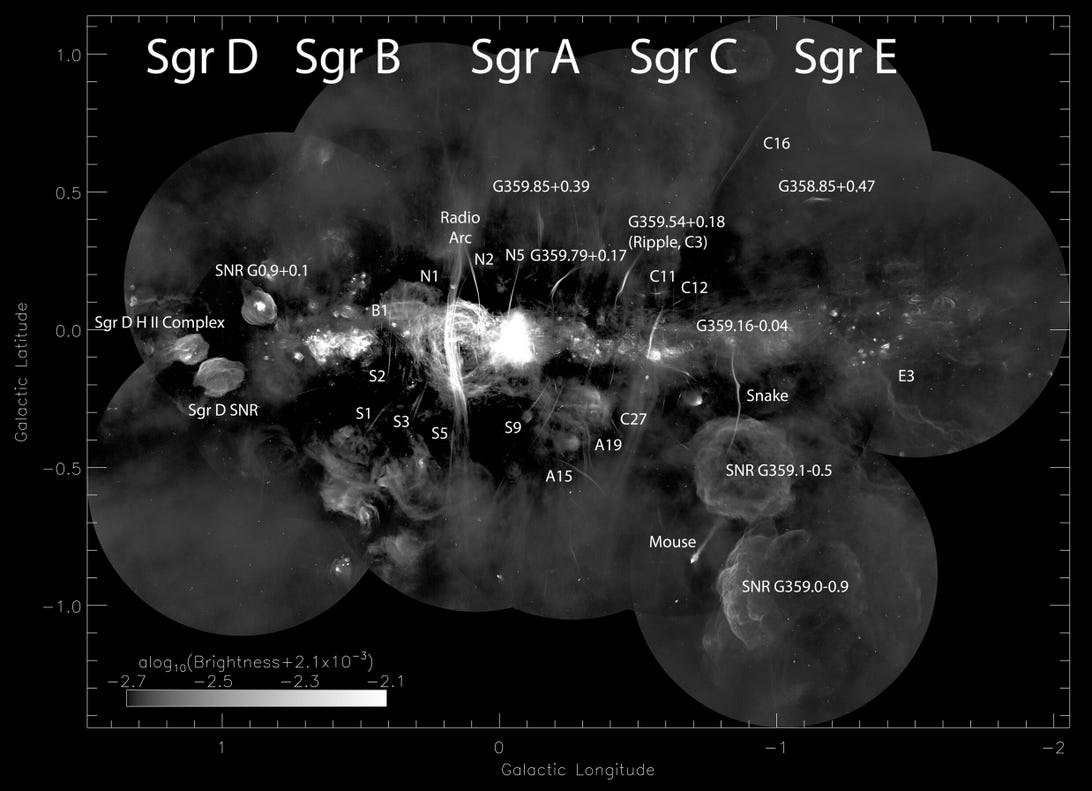
A mosaic symbol (with labels) of the middle of the Milky Manner, captured with radio waves. That is sooner than the background was once got rid of. On this image, the magnetic filaments are massive, vertical slashes all over.
Northwestern College/Saoro/Oxford College
Then, the researchers pieced the cutouts in combination and remoted the magnetic filaments via getting rid of the background. That resulted in the captivating mosaic {photograph} that resembles a Jackson Pollock.
“I have spent a large number of time taking a look at this symbol within the technique of operating on it, and I by no means get bored of it,” Ian Heywood, an astrophysicist at Oxford College and learn about co-author, stated in a observation. “Once I display this symbol to those who may well be new to radio astronomy, or in a different way unfamiliar with it, I all the time attempt to emphasize that radio imaging hasn’t all the time been this fashion, and what a soar ahead Meerkat actually is in relation to its functions.”
Leads at the filaments
Now blessed with an ocean of inexplicable Milky Manner filaments to research, Yusef-Zadeh and group are sporting out a form of inhabitants research to know what the cosmic spaghetti strands have in not unusual, and the place they range.
“If you happen to had been from some other planet, for instance, and also you encountered one very tall particular person on Earth, you may think all individuals are tall. However when you do statistics throughout a inhabitants of other folks, you’ll in finding the common top,” he stated. “That is precisely what we are doing. We will be able to in finding the power of magnetic fields, their lengths, their orientations and the spectrum of radiation.”
Up to now, the group concludes the strands’ magnetic fields are amplified as you journey throughout them and showcase variation of their radio emissions. Because of the latter, they are saying the items may just’ve originated from a black hollow that when lurked within the heart of our galaxy or a large radio-emitting bubble, like one found out in 2019.
Nonetheless, large query marks stay, akin to why are those filaments so structured? And why are there such a lot of? Possibly the most important confusion lies inside the truth that debris at the strands’ box are shifting at just about the rate of sunshine. Any sooner, and they might have compatibility a time-travel requirement.
“How do you boost up electrons at with reference to the rate of sunshine?” Yusef-Zadeh wonders. “One thought is there are some assets on the finish of those filaments which might be accelerating those debris.”
Going ahead, the group says they’re going to proceed looking for solutions.
“We are indisputably one step nearer to a fuller figuring out,” Yusef-Zadeh stated. “However science is a sequence of development on other ranges. We are hoping to unravel it, however extra observations and theoretical analyses are wanted. A complete figuring out of advanced gadgets takes time.”
